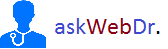
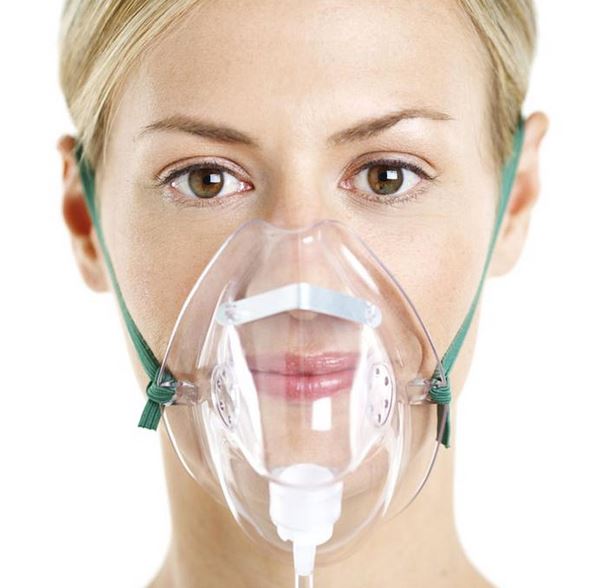
Usually, oxygen is given via facemask or nasal cannula. The physician should prescribe the oxygen administering method. This avoids administration of too much or too little oxygen. Oxygen saturation of blood is monitored, the screen of the monitor shows the level of oxygen saturation. The aim should be keeping the O2 Sat more than 94%. In case of a COPD patient or a patient who is at risk of developing hypercapnia, keep the O2 saturation aim between 88 and 92%.Let us discuss the various options that can be used to administer Oxygen in a clinical setting and what are the hazards and benefits of individual delivery methods.
Nasal Canula
Oxygen delivery via nasal cannula is preferred by the patients. But oxygen delivery by this method is imprecise. It may cause nasal soreness in patients. The supported oxygen flow rate is 1-4L/min which roughly delivers 24-40% FiO2. Increasing the flow rate beyond 4L/min doesn’t increase the FiO2. This method is preferably used in COPD patients (if venturi masks are not available) because a low FiO2 can be safely delivered using this method and also patients can be nebulized easily.
Face Mask

- Simple face mask
Facemask delivers a variable amount of oxygen depending upon the flow rate. This is usually used for short time and in the emergency situations. It is very imprecise so is not very suitable for using in case of COPD patients or in those patients who are at risk of developing hypercapnia. In case of Face mask the flow rate shouldn’t be less than 5L/min. Flow rate of less than 5L/min causes accumulation of Carbon dioxide within the mask and in the inspired air.
Points to Remember
- Keep oxygen flow rate more than 5L/min in case of simple mask.
- For COPD patients, Venturi mask is the best option for oxygen administration.
- Venturi masks can deliver up to 60% FiO2.
- Non-rebreathing can deliver up to 90% FiO2.
- Humidification is required for long-term delivery of O2 at high flow rate and tracheostomies.
- Humidification may increase the secretions and expectoration.
- Keep oxygen flow rate more than 10L/min in case of using a nonrebreathing mask.
Venturi Mask

Venturi masks are very accurate and should be used when available. These masks are specially designed and provide a precise percentage of FiO2 in high flow rates. These are available in various color codes and each color represents a percentage of FiO2.
- Blue: 24%
- White: 28%
- Yellow: 35%
- Red: 40%
- Green: 60%
This is a perfect mask for COPD patients. Start with the venturi with FiO2 of between 24 and 28%. Nasal cannula can be used in those cases where venturi mask is not available.
Nonrebreathing Mask
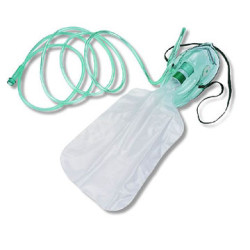
Non-rebreathing masks come with an attached reservoir bag. These are used in emergency and in those patients where controlled delivery of oxygen is not required. These masks can deliver 60-90% FiO2 depending upon the flow rate. The minimum flow rate for a non-rebreathing mask is 10L/min. At 10L/min, it delivers 60% FiO2 and at 15L/min it may deliver up to 90% FiO2. Nonrebreathing mask is used in emergency situations and is not suitable for those patients who require low dose or controlled oxygen therapy.
Other Measures
Other measures include management of underlying contributing factors such as anemia, heart failure or excessive secretions. If patient has underlying anemia, correct it with the help of blood transfusion if patient has got acute hypoxia. Treat heart failure and continue chest physiotherapy in order to promote oxygen delivery and saturation.