Tuberculosis is a pulmonary or lung infection. It is a chronic infection, it needs a long treatment course. If you are suffering from tuberculosis and you are wondering why tuberculosis treatment course is so long? In order to answer this question, first we should know about the bacteria which is responsible for causing tuberculosis.
Read this article “Why Does Mycobacterium Tuberculosis need long treatment course?”
After reading this article, now you know why you need long term treatment. But before discussing the treatment lets us discuss few signs and symptoms of Tuberculosis and when should you start thinking that you might be suffering from tuberculosis
Signs and Symptoms:
The most common signs and symptoms of tuberculosis are;
- Fever, usually low-grade, but long term, with intermittent high-grade episodes.
- Night Sweats, a common symptom
- Cough, a cough that lasts more than 2 weeks, strongly raise the suspicion of Tuberculosis.
- Weight loss, another common symptom, the patient feels weak, eats less and loses weight over the period of weeks.
- Chest pain and shortness of breath, Patient may feel chest pain on and off, usually upon exertion, shortness of breath is also a symptom which becomes more prominent upon exertion.
So in conclusion, if you have fever, night sweats, you eat less and you have a more than 2 weeks long history of cough then you should immediately see your doctor, as tuberculosis is one of the top differential diagnoses in this case.
What should you expect from your doctor?
Your doctor will ask you some question, will take a detailed history and also will examine you. Examination alone usually doesn’t provide a conclusive information, so doctor order some tests. Your doctor may order the following tests.
- Chest X-Ray: Chest X-Ray helps to assess the condition of the lungs. Usually, lungs appear black on Chest X-Ray film. In case of an infection or tuberculosis, doctor sees white patches on the X-Ray film.
Positive Tuberculin Test - Sputum for AFB: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is an acid-fast bacillus (AFB), Sample of sputum is examined under a microscope using special staining techniques. If acid-fast bacilli are seen under the microscope, then it confirms the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
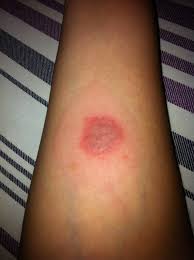
- Tuberculin Test also called Mantoux Test: In tuberculin test, a solution called PPD is injected under the skin of the forearm. The injected area is then examined after 3 days. If the injected area is swollen or indurated, then it means, the patient is exposed to Tuberculosis causing bacteria that is Mycobacterium Tuberculosis.
- TB Blood tests, called QuantiFERON TB Gold and T-Spot Test: These are two blood tests which are also confirmatory and your doctor may order these.
Choice of the Test
Choice of test entirely depends on the doctor’s point of view. All of these tests are confirmatory and if one test comes negative and your doctor still suspect TB then he may order another test to confirm.
If none of the tests comes positive, but clinically your doctor still think that you have tuberculosis, then he should start you on anti-tuberculous treatment and you should complete the course.
Treatment
Treatment is simple but is of long duration. Depending on the geographical area of the world, treatment duration varies from six to nine months.
First two months of treatment is called intensive phase of treatment. This is called intensive phase because in this phase four drugs are given. Drugs include:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
After two months, sputum test is done, if now AFB is seen in the sputum, then the patient is started on continuation phase. In continuation phase, two drugs are given for the period of 4-7 months.
- Isoniazid
- Pyrazinamide
If sputum test comes positive after two months, then the intensive phase is continued for another month. After a month, another sputum AFB is done, if it comes negative then pt is started on continuation phase. If it again comes positive then the patient should be referred to a chest specialist to start on Multi-Drug Resistant Treatment Regimen.